Chemicals shape the way we live, work, and innovate, and among them, butanone stands as a highly versatile compound. Known scientifically as methyl ethyl ketone (MEK), it belongs to the ketone family and has gained global importance because of its wide use across industries. From solvents to adhesives, butanone plays an essential role in production, research, and chemical applications. Understanding this compound requires a closer look at its structure, behavior, and impact on daily life.
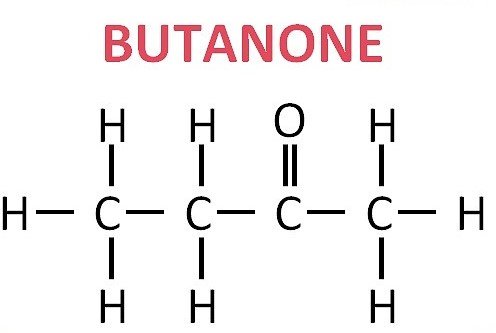
Chemical Structure and Formula of Butanone
To understand why butanone is so useful, we must examine its molecular composition.
-
Formula: C4H8O
-
Molecular Weight: 72.11 g/mol
-
Structure: A four-carbon chain with a carbonyl group located at the second carbon atom
This carbonyl placement makes it a ketone rather than an aldehyde. The position contributes to its reactivity and stability, which explains why it is chosen as a solvent in many industries.
Physical Properties of butanone
The popularity of butanone comes from its balanced physical properties.
-
Appearance: Colorless liquid
-
Odor: Sweet yet sharp, similar to acetone
-
Boiling Point: Around 79.6 °C (175 °F)
-
Melting Point: −86 °C (−123 °F)
-
Solubility: Miscible with most organic solvents, partly soluble in water
Because of these properties, butanone can dissolve a broad range of substances while remaining easy to handle in industrial settings.
How Butanone Is Produced
Industrial production of butanone typically relies on large-scale chemical reactions.
-
Dehydrogenation of 2-Butanol
This method involves the catalytic removal of hydrogen from 2-butanol, yielding butanone as the main product. -
Oxidation of Butane
Butane undergoes catalytic oxidation, producing butanone among other byproducts. -
Fermentation-Derived Methods
Though less common, some biotechnological approaches use microorganisms to synthesize butanone from renewable feedstocks.
Uses of butanone in Everyday Life and Industry
The compound’s versatility explains why it is so widely adopted across multiple industries.
-
As a Solvent: Essential in paints, coatings, adhesives, and varnishes.
-
In Plastics Production: Helps process resins and polymers.
-
In Rubber Manufacturing: Improves flexibility and durability.
-
In Printing Inks: Ensures smooth application and fast drying.
-
In Cleaning Agents: Applied in degreasing and industrial cleaning operations.
-
In Chemical Synthesis, used as an intermediate to create other compounds.
Benefits of Using butanone
The value of butanone lies not only in its effectiveness but also in its efficiency.
-
High Solvent Power – Dissolves many substances that water or alcohol cannot.
-
Fast Evaporation Rate – Useful in coatings and paints that require quick drying.
-
Versatility Across Industries – From plastics to pharmaceuticals, its role is diverse.
-
Compatibility with Other Chemicals – Can be blended easily to enhance performance.
Safety Concerns and Precautions
Like many industrial chemicals, butanone must be handled carefully. Safety is critical when working with it in laboratories or factories.
-
Inhalation Risks: High concentrations may irritate the respiratory system.
-
Skin and Eye Contact: Can cause dryness or irritation.
-
Flammability: Highly flammable and should be stored away from heat or sparks.
-
Long-Term Exposure: May affect the nervous system if proper precautions are not followed.
Recommended Safety Measures
-
Use protective gloves, goggles, and masks when handling butanone.
-
Ensure proper ventilation in working areas.
-
Store in tightly closed containers away from open flames.
-
Follow workplace chemical safety regulations to reduce risk.
Comparison of butanone with Other Ketones
To understand the role of butanone, it helps to compare it with similar compounds.
-
Butanone vs. Acetone: Both are strong solvents, but acetone evaporates faster and is more water-soluble. Butanone, however, is less volatile and often preferred in coatings.
-
Butanone vs. Propanone: Propanone is another name for acetone, again highlighting that butanone has slightly stronger solvency and longer drying time.
-
Butanone vs. Pentanone: Pentanone has higher boiling points and lower volatility, making butanone more desirable for applications needing rapid evaporation.
Environmental Impact of butanone
Although butanone has valuable uses, its environmental impact must not be overlooked. It can contribute to air pollution when released in large amounts, and improper disposal may contaminate soil and water. Therefore, industries are encouraged to use sustainable disposal methods, recycle solvents where possible, and adopt greener alternatives when available.
Future of butanone in Industry
The role of butanone in industry will likely evolve. As sustainability becomes more important, research is being directed toward eco-friendly production methods, including biobased synthesis. Additionally, industries are exploring ways to recycle solvents more effectively, which will make butanone usage safer and more sustainable in the long run.
Conclusion
Butanone, also known as methyl ethyl ketone, is more than just another chemical in the catalog of industrial solvents. Its balance of properties makes it indispensable in paints, coatings, plastics, adhesives, and cleaning products. Yet, its flammability and health risks mean responsible handling is essential. By using it wisely, industries can maximize its benefits while minimizing harm to people and the environment. In the future, innovations in green chemistry may provide cleaner, safer ways to produce and use butanone while keeping its unique strengths intact.